The auxiliary drive tensioner is a high-precision element designed, as its name suggests, to optimize the tension of the accessory belt and also prevent future failures in the other components such as the alternator or the pump.
In today’s article, we will learn how it works, the different types that we find on the market and the importance of this key element for the accessory drive system.
How does a belt tensioner work?
As we have seen in previous articles, the auxiliary drive belt transmits rotational energy from the engine crankshaft to all engine accessories.
What happens is that, during the operation of the auxiliary drive system and as our vehicle’s engine speeds up and slows down, the belt can stretch or even lose some tension, hence the importance of the tensioner pulley within this system.
The aux drive tensioner or serpentine belt tensioner is, therefore, an element responsible for exerting a regulated amount of pressure/tension on the belt and thanks to this the belt can rotate all those pulleys as needed.
Potentially, its main function is to guarantee that the auxiliary belt has the optimum tension, although among its basic functions we also find:
- Maintain the correct and tight tension on the pulley by compensating for any possible loss of tension in the auxiliary belt.
- Maintain correct alignment with the rest of the accessory belt drive system.
- Avoid slipping and vibrations that cause premature wear of the elements and that avoid fatigue in the auxiliary belt.
Keep learning: Understanding the Drive Belt Tensioner
Main types of drive belt tensioners
As auxiliary drive belts with poly-V belts, tensioners have also been upgraded in recent years. The two most common types of tensioners in the auxiliary drive system are hydraulic tensioners and mechanical tensioners, the last one being able to be manual or automatic. Let’s see its characteristics below:
Mechanical Tensioner
This type of tensioner can be subdivided into manual tensioners, where the mechanic will be in charge of providing the correct prescribed tension manually, and automatic tensioners.
Automatic tensioner is the most common tensioner on the market. This tensioner is characterized by the fact that it adjusts itself according to the need of the moment and its working conditions.
It has a spring located inside with an oscillating arm that maintains pressure on the belt and moves always keeping the strap in place.
Hydraulic Tensioner (with hydraulic shock absorber)
In this case, the hydraulic tensioner is based on a hydraulic shock absorber that stands out for its high performance, exerting precise tension and dynamic behavior. It can operate with a larger range of dynamic belt lengths than mechanical tensioners.
These tensioners have an arm and a roller at the ends, and it is through the hydraulic element with an integrated pressure spring that they achieve the necessary belt tension.
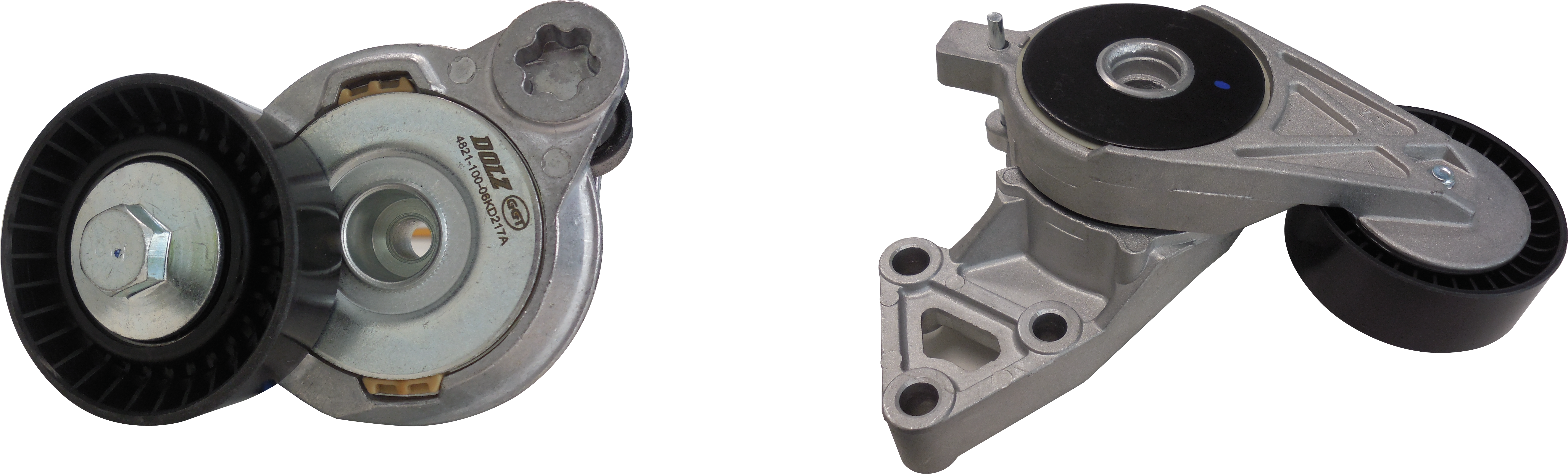
Belt tensioner failure signs
A damaged or faulty tensioner will directly affect the performance and functionality of the auxiliary drive belt and will cause the entire system early failure. In general, a tensioner that does not work as it should show some warning signs. Among the most common signs and causes are:
- Squeaking noise or unusual noise when starting the engine or during operation when the steering is turned all the way to one side. If the tensioner is loose and not exerting pressure, aux belt can squeak.
- Accessories failure. If any of the engine accessories such as the alternator, air conditioner compressor or power steering are disengaging, this may be caused by a bad or faulty tensioner.
- Premature aux belt failure. If you notice unusual wear on the serpentine belt, such as frayed edges or cracks in the belt itself, this is due to a malfunction of the drive belt tensioner.
Keep learning: Top 5 causes of serpentine belt failure
Too often, when the auxiliary belt shows signs of aging and needs to be replaced, it is overlooked to inspect the well condition and function of the other elements, including the drive belt tensioner. This error can cause premature wear of the serpentine belt and a new replacement operation.
All components are subject to stresses and wear, so during the auxiliary belt replacement process, it is highly recommended replace all components at the same time. This ensures optimal operation and longer lasting performance.
Dolz Kits, the most competitive kits on the market
Industrias Dolz has a complete range of Auxiliary Drive Belt Kits, designed following the experience of original manufacturers such as Audi, Volkswagen, or Renault to guarantee the best engine performance and the greatest comfort.
These kits include all the necessary components for a professional repair, that is, all in one package: poly-V belt, tensioning rollers, inversion and all the necessary accessories depending on the vehicle application.
For further information on any of our product lines, commercial information, or technical product specifications (including replacement guidelines) you can contact us here.


